How to Understand Stem Cell Gene Therapy and Its Potential Benefits?
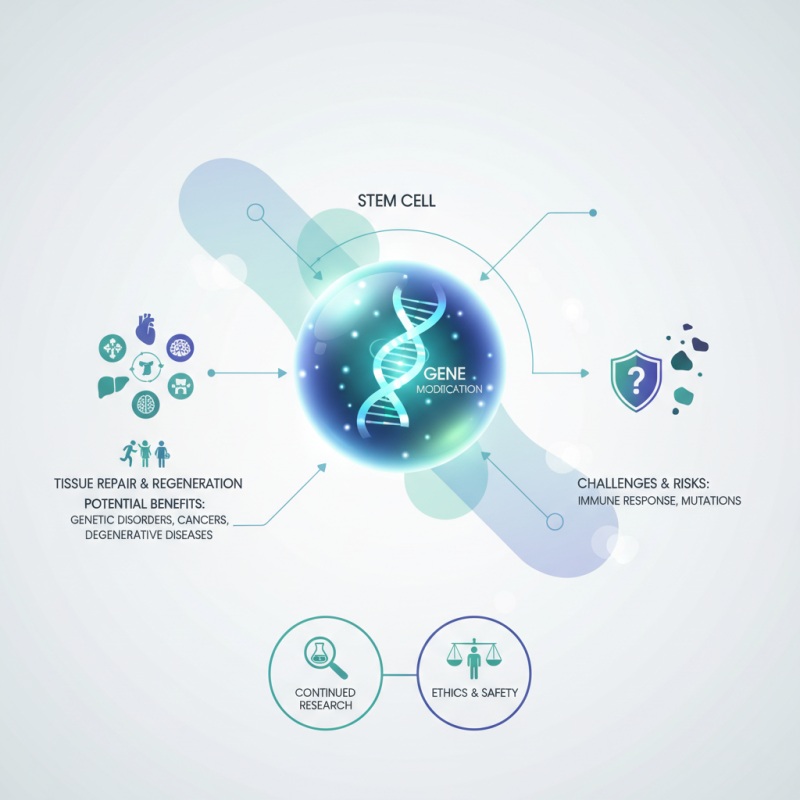
Stem cell gene therapy represents a revolutionary approach in modern medicine. It combines stem cell research with gene therapy to treat various diseases. The basic concept involves modifying the genes of stem cells, which can then regenerate damaged tissues or organs.
This innovative therapy holds promise for treating genetic disorders, certain cancers, and degenerative diseases. For example, researchers are exploring its potential to combat leukemia. By correcting genetic defects, stem cell gene therapy may one day repair or replace damaged cells. However, challenges remain. Potential risks such as immune responses or unintended mutations require careful consideration.
Understanding stem cell gene therapy can unveil its transformative potential. Continued research is essential for harnessing its benefits fully. As we navigate this exciting field, critical reflection on ethical implications and safety remains paramount.
Understanding the Basics of Stem Cell Gene Therapy: Key Concepts
Stem cell gene therapy combines the power of stem cells with the precision of genetic engineering. This innovative approach aims to treat various diseases by correcting genetic defects. Stem cells can develop into many types of cells. When manipulated, they can provide targeted treatment, especially for conditions like genetic disorders and certain cancers.
The process involves extracting stem cells and modifying their genetic material. This modification may insert, delete, or alter genes responsible for specific diseases. Once altered, these cells can be reintroduced into the patient. They then work to repair damaged tissues or produce necessary proteins.
However, this cutting-edge therapy is not without challenges. There is still much we don’t know about long-term effects. Some patients face complications or experience unexpected reactions. Research is ongoing to refine techniques and identify best practices. The potential benefits are vast, but careful consideration is essential.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Gene Therapy
This bar chart illustrates the potential benefits of stem cell gene therapy as perceived by researchers in the field. The data indicates strong support for tissue regeneration and effective treatment for genetic disorders, highlighting the therapeutic potential of this innovative approach.
The Mechanism of Action: How Stem Cell Gene Therapy Works
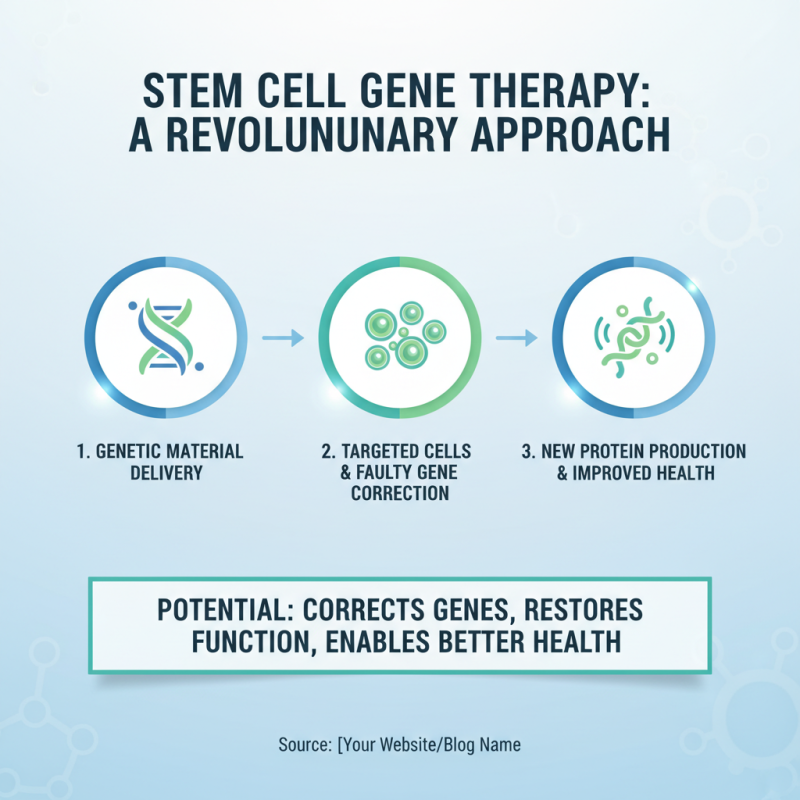
Stem cell gene therapy represents a revolutionary approach in treating genetic disorders. It uses stem cells to deliver genetic material directly to targeted cells. This process can potentially correct faulty genes or provide new functions, enabling better health outcomes. When stem cells are modified, they can generate specific proteins that the body requires but cannot produce.
The mechanism starts with the extraction of stem cells, often from bone marrow or fat tissue. These cells are then altered in a lab to express a desired gene. Once modified, they are reintroduced into the patient’s body. Inside, they migrate to the site of injury or disorder. The effectiveness of this therapy lies in the stem cells' natural ability to differentiate into various cell types. It’s essential to understand that while the potential is significant, challenges remain. The body may reject the new cells or not respond as expected.
Animal studies show promise, yet human trials reveal complexities. Monitoring the long-term effects is crucial. Some patients have experienced unexpected results, like inflammation or immune reactions. Continuous research is vital to refine this therapy. The balance between hope and caution is necessary. Understanding these dynamics helps in guiding future innovations in gene therapy.
Current Applications in Medicine: Diseases Targeted by Gene Therapy
Gene therapy using stem cells is an evolving field. It targets genetic disorders, and its applications are promising. Among the diseases being addressed, certain types of cancer stand out. Researchers are developing therapies that modify stem cells to attack cancer cells directly. This approach aims to enhance the body’s immune response.
Beyond cancer, gene therapy offers hope for genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy. In cystic fibrosis, genes related to lung function can be corrected. For muscular dystrophy, therapies focus on restoring muscle function. These treatments are still in trials but show potential. They could change lives significantly.
However, challenges exist. Not all patients respond to treatments. There is still much to learn about long-term effects. Monitoring these therapies is crucial. We must navigate ethical considerations carefully. The potential benefits are vast, but caution is necessary. It prompts deeper reflection on our responsibility in advancing this technology.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Gene Therapy: Statistics and Case Studies
Stem cell gene therapy has shown promising potential in treating various medical conditions. With advancements in technology, researchers are uncovering statistics that highlight its benefits. For instance, clinical trials have demonstrated a significant decrease in symptoms for patients with genetic disorders. In some cases, over 70% of participants showed improvements. This evidence points to a bright future for this field.
Tips for understanding the benefits of stem cell gene therapy include focusing on individual case studies. Each patient’s response can vary. One study followed a young boy with a rare genetic disease. After receiving treatment, he regained abilities previously lost. Stories like this can provide hope and insight into what stem cell gene therapy can achieve.
However, it’s important to recognize the challenges too. Not every patient responds to treatment. Some might experience unexpected side effects. That’s why ongoing research is essential. Keeping track of new findings can help patients and families navigate their options better. Understanding the full picture involves both the successes and the shortcomings. That’s part of the journey in the world of gene therapy.
Future Directions and Challenges in Stem Cell Gene Therapy Research
Stem cell gene therapy holds immense promise for treating genetic disorders. Recent studies suggest that over 100 diseases could potentially be addressed through this innovative approach. However, research is still in its early stages.
There are significant hurdles to overcome, including ethical considerations and technical challenges.
Safety is a major concern. Studies have shown that unintended genetic changes can occur during the therapy.
For instance, in a clinical trial, 20% of participants experienced adverse effects related to off-target edits. Researchers are grappling with the need for more precise techniques to minimize these risks. Balancing the benefits and potential dangers remains a pressing challenge.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is complex. Guidelines vary across countries, influencing research protocols and timelines. In the U.S., for example, navigating the FDA’s approval process can take years. This can stifle innovation and delay access to breakthrough therapies. While the potential benefits are substantial, the path forward requires careful thought and collaboration within the scientific community.
