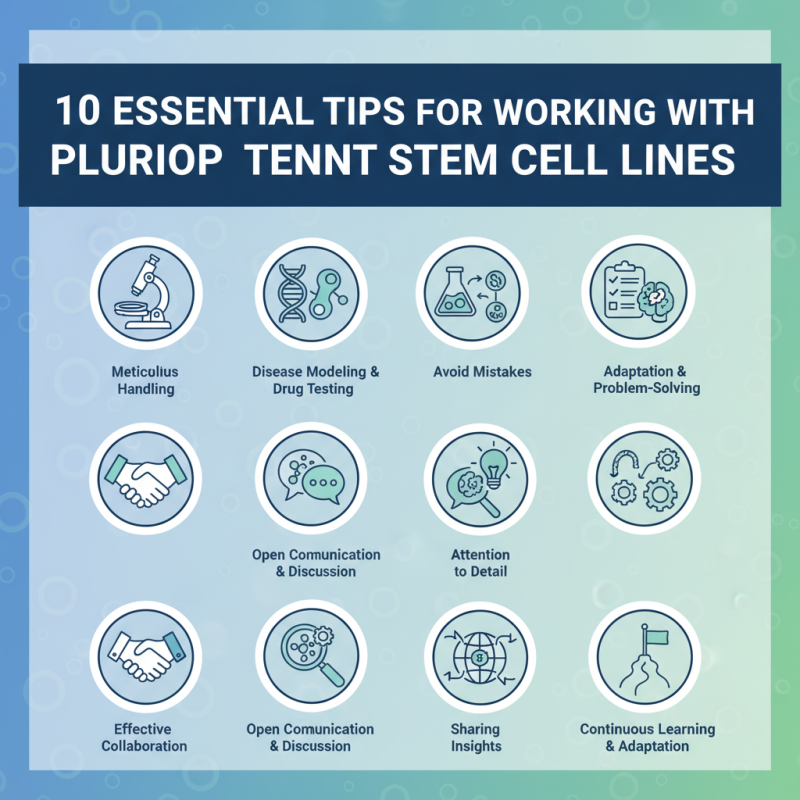
10 Essential Tips for Working with Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines
In the field of regenerative medicine, working with pluripotent stem cell lines is both promising and challenging. Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in stem cell biology, once stated, “The potential of pluripotent stem cell lines lies in their ability to differentiate into any cell type.” This underscores the importance of understanding these cells for advancing therapies.
Pluripotent stem cell lines require meticulous handling. These cells offer unprecedented opportunities in disease modeling and drug testing. However, researchers often face challenges related to maintenance and differentiation. The protocols can be complex and inconsistent. Mistakes can lead to failed experiments or unreliable results. Adapting to these challenges is key to successful outcomes.
Effective collaboration among researchers can drive innovation. Open discussions about difficulties can lead to novel solutions. Sharing insights improves the overall quality of work with pluripotent stem cell lines. Emphasizing attention to detail and open communication is essential in this evolving field. The journey with pluripotent stem cell lines is filled with learning and adaptation.
Understanding Pluripotent Stem Cells: An Overview of Their Properties
Pluripotent stem cells have unique properties that make them a hot topic in research. They can differentiate into nearly any cell type. This potential has broad applications, from regenerative medicine to disease modeling. However, working with these cell lines can be complex and challenging. Researchers must navigate variability in cell behavior and ensure consistent results.
Understanding their biology is crucial. Pluripotent stem cells originate from the inner cell mass of blastocysts. This origin influences their capabilities. They can self-renew indefinitely in culture, but controlling this process requires careful attention. Sometimes, they may undergo spontaneous differentiation. Such unpredictability can affect experimental outcomes.
Researchers often reflect on their methods and results. A careful balance of culture conditions is key. Environmental factors, like oxygen levels, impact cell health. Fine-tuning these elements can lead to more reliable results. Still, unexpected challenges may arise, prompting further investigation. These reflections are essential for improving techniques and advancing the field.
Choosing the Right Pluripotent Stem Cell Line for Your Research Needs
Choosing the right pluripotent stem cell line can significantly impact your research outcomes. Consider the specific goals of your study. Different cell lines may exhibit distinct characteristics, such as growth rates, differentiation potential, and genetic profiles. It’s essential to match the cell line’s traits with your experimental needs.
Evaluate the source of your stem cell line. Some lines may be derived from different species or developmental stages. This factor can influence your results and their applicability. Additionally, think about the availability of resources and support for the chosen line. Limited resources could hinder your progress.
Collaboration is key. Engaging with other researchers can provide valuable insights. Discuss their experiences with various cell lines. Reflect on their successes and struggles. It may inform your decision-making process and help identify potential challenges early on. Alternatively, consider the possibility of using multiple lines to cross-validate results. Embracing a flexible approach can lead to more robust findings.
Essential Laboratory Techniques for Culturing Pluripotent Stem Cells
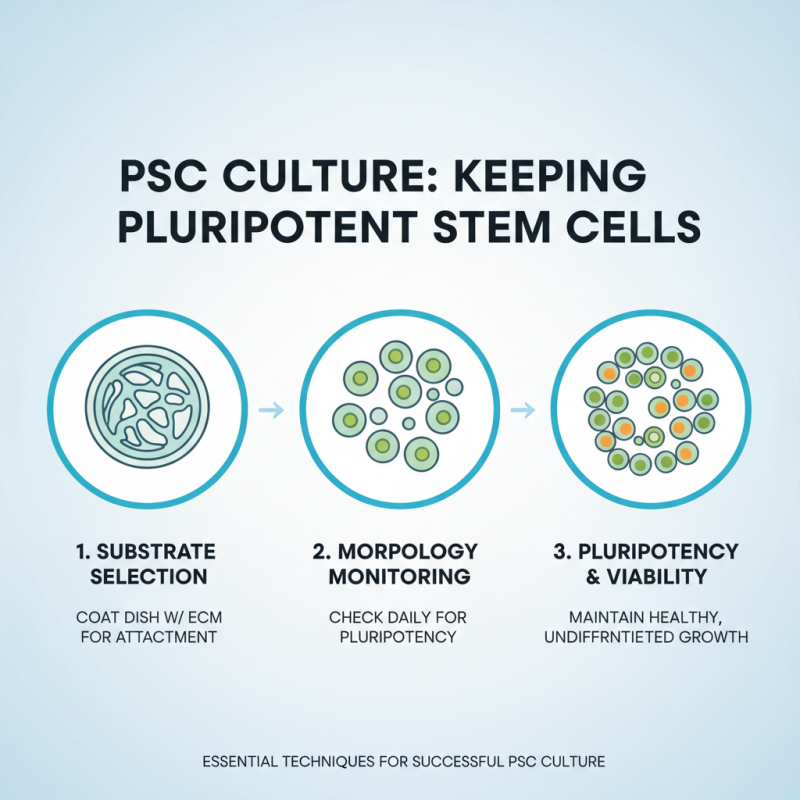
Culturing pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) is a complex yet rewarding process. Proper techniques are essential to maintain their pluripotency and viability. It starts with selecting the right substrate. Coating a culture dish with extracellular matrix allows cells to adhere and grow better. Regularly checking cell morphology is crucial. Changes may indicate that the cells are losing their pluripotent characteristics.
Another key technique is media preparation. The culture medium should be enriched with growth factors to support PSC growth. However, even slight variations in pH or temperature can lead to cell stress. It can be tricky to find the perfect balance. Regular media changes can also help maintain cell health but may risk damaging sensitive cells during transfer.
Finally, passaging techniques cannot be overlooked. Cells should be gently detached from their substrate to avoid damage. Over-trypsinization or mechanical stress can lead to cell death. Keeping a close eye on cell density is vital. If cells become too confluent, it may hinder their growth potential. It's a balancing act that requires constant adjustment and reflection.
Maintaining Pluripotency: Key Factors and Conditions for Success
Maintaining pluripotency in stem cell lines is crucial for research and therapy. Key factors include precise control of culture conditions and regular monitoring. Recent studies indicate that over 40% of pluripotent stem cell lines lose their pluripotency without proper maintenance. This underscores the importance of vigilant care.
One effective tip is to optimize the feeder layer. Utilizing an appropriate matrix can significantly enhance cell growth and pluripotency. However, researchers often overlook how subtle changes in the environment affect cell behavior. Monitoring pH and oxygen levels is essential. These elements can influence gene expression and differentiation pathways.
Another tip is regular passaging. Cells should be split before reaching 80% confluence. Delaying passaging can lead to chromosomal instability. Accurate timing and technique are paramount in maintaining healthy, pluripotent populations. Documentation of growth rates and media conditions allows for reflection and adjustment, ensuring optimal cell line performance.
10 Essential Tips for Working with Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines - Maintaining Pluripotency: Key Factors and Conditions for Success
| Tip | Description | Key Factors | Conditions for Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Maintain a Sterile Environment | Ensure all procedures are performed in a sterile condition to prevent contamination. | Aseptic Technique | Use laminar flow hoods and sterile consumables. |
| 2. Optimal Culture Conditions | Culturing cells in a medium that supports pluripotency. | Growth Factors | Use defined media with necessary supplements. |
| 3. Regular Passaging | Frequent subculturing to avoid over-confluence. | Cell Density | Passage when cells reach 70-80% confluence. |
| 4. Monitor Cell Morphology | Regularly check cells under a microscope. | Cell Health Assessment | Look for colonies with a clear and defined shape. |
| 5. Use of Appropriate Coating | Coat dish surfaces to enhance cell attachment. | Extracellular Matrix Components | Utilize Matrigel or collagen. |
| 6. Genetic Stability | Screen for genetic abnormalities regularly. | Karyotyping | Perform periodic karyotype analysis. |
| 7. Maintain Pluripotent Markers | Regularly check expression of pluripotency markers. | Marker Analysis | Use flow cytometry or immunostaining. |
| 8. Avoid Differentiation Stress | Minimize exposure to differentiation signals. | Environmental Factors | Control CO2 levels and temperature precisely. |
| 9. Updated Protocols | Keep up-to-date with latest protocols and publications. | Literature Review | Join research communities and forums. |
| 10. Staff Training | Ensure all staff are well-trained in stem cell handling. | Education and Training | Conduct regular training sessions and refreshers. |
Ethical Considerations in the Use of Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines
Working with pluripotent stem cell lines raises important ethical concerns. The source of these cells often comes from human embryos, creating a debate about consent and the moral implications of using human life. Researchers must consider the rights of donors and the necessity of informed consent. What measures are in place to ensure that these donors fully understand the implications of their contributions?
The use of these cell lines also brings about questions of exploitation. Are we taking advantage of vulnerable populations for their biological material? The guidelines for ethical research must protect these groups. Furthermore, scientists should reflect on the long-term impacts of their work. How do we balance scientific progress with ethical considerations? Every new discovery can lead to unforeseen consequences.
It’s critical to foster a culture of responsibility in the laboratory. Researchers must engage in continuous dialogue about ethics and refine their practices. Engaging diverse stakeholders in this conversation may create a more inclusive approach to stem cell research.